Cross Section Elements
Cross-section elements of the road include carriageway, shoulder, median, lateral clearance, vertical clearance, kerb, and guard rail which are discussed in the following subsections.
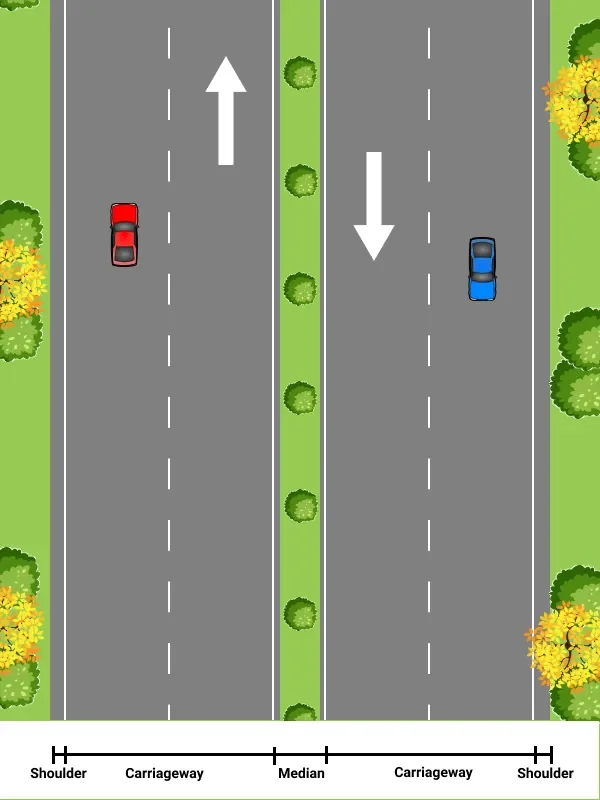
Carriageway
It is the width of a road, which is used for the movement of vehicular traffic. In general, you are not supposed to stop your vehicle on the carriageway because it will interrupt the traffic flow and lead to congestion. Stopping on a carriageway is also unsafe.
Shoulder
The shoulder is the width of a road adjacent to the main carriageway. It is provided to facilitate emergency stopping of a vehicle. In the event of an emergency or breakdown, you should pull your vehicle to the shoulder without blocking the main carriageway. On some roads, the shoulder is paved and demarcated by a solid white line between the shoulder and the carriageway. On many other roads, the shoulder is unpaved. You should carefully assess the condition of the unpaved shoulder before parking your vehicle.
Median
The median is the longitudinal space provided to separate the traffic streams moving in opposite directions. It is also used to install lights and traffic signs. Small bushes are often planted on the median to avoid the glare of lights from the traffic coming from the opposite direction. As a driver, you need to note the following: • Often medians are separated from the carriageway using raised kerb (a kind of physical barrier). So, while using the innermost lane (adjacent to the median), you should be extra careful not to lose control of the vehicle. An uncontrolled vehicle may hit the median and cause an accident. • You must respect the direction of travel and must not travel in the wrong direction causing contraflow. Always drive keeping the median on your right side. You should not hesitate to travel additional distances (instead of causing contraflow) for the sake of your safety and the safety of other road users.
Lateral Clearance
Lateral clearance is the distance between the extreme edge of the carriageway and the nearest face of the obstruction. Hence, while driving on the extreme edge of the carriageway (especially on narrow bridges), assess the available lateral clearance and drive cautiously to avoid collision with the obstruction.
Vertical Clearance
Vertical clearance is the vertical distance between the highest point of the carriageway to the lowest point of the overhead structure. The roadway facilities are designed considering the physical dimension of vehicles (say, height, width, etc.). However, in some cases, the available vertical clearance may not be adequate for larger vehicles like trucks or buses. As a driver, it is your responsibility to assess the available vertical clearance (in the absence of a sign) and ensure the safe passage of your vehicle. Also, it is your duty not to overload your vehicle (especially for commercial vehicles) or allow rooftop travel (especially for buses) with an added emphasis on safety while crossing an underpass.
Kerb
