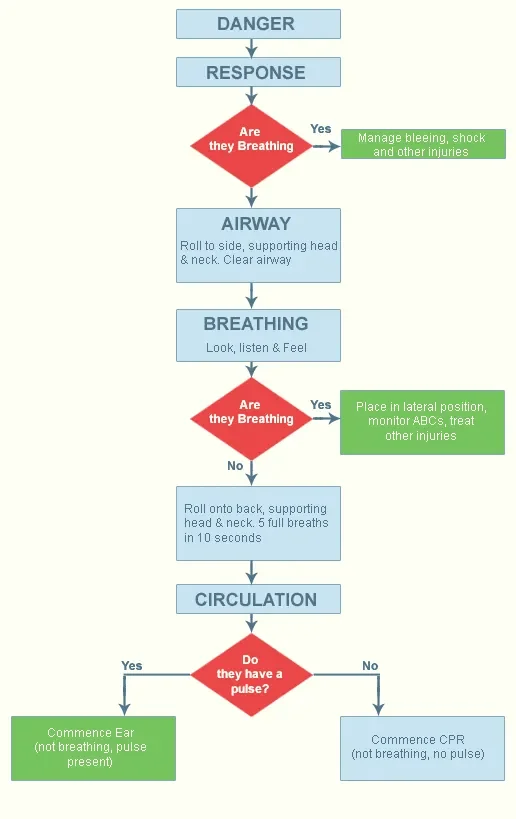
Treatment of Shock
After an injury, the accident victim may enter into a shock. In that case, you must take quick action through the following steps:
- SHAKE & SHOUT: You can do this by gently shaking their shoulders and by saying “Hello, can you hear me?” If the person does not answer, it means that the person is unconscious.
- CALL FOR HELP: You must then call for help. If there is a bystander, ask him to call an ambulance and assist you. If there is no one, you must call for an ambulance by dialing 112 or 102 as any unconscious casualty needs to go to the hospital.

- Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): CPR is the skill necessary to artificially provide circulation of blood to the brain and air to the lung in order to prevent damage to the brain. It is only performed on someone who is unconscious, not breathing, no pulse or sign of circulation. It is done until any medical help arrives.
Steps of Providing CPR

- Step 1: The victim should be laid down flat on a hard surface.
- Step 2: You (the rescuer) should kneel beside the victim’s chest.
- Step 3: Clean the victim’s mouth and remove any foreign body or artificial denture.
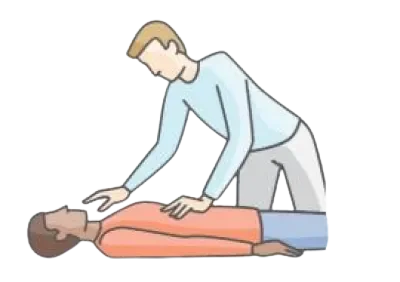
- Step 4: Place the heel of the hand on the centre of lower part of the sternum (breastbone). Put the heel of another hand on the top of the first hand.
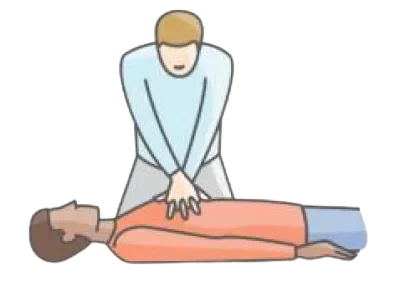
- Step 5: Keep arm straight, elbow locked and interlock fingers to avoid compression on the ribs. Now push down at least 2 inches at a rate of at least 100 times per minute.
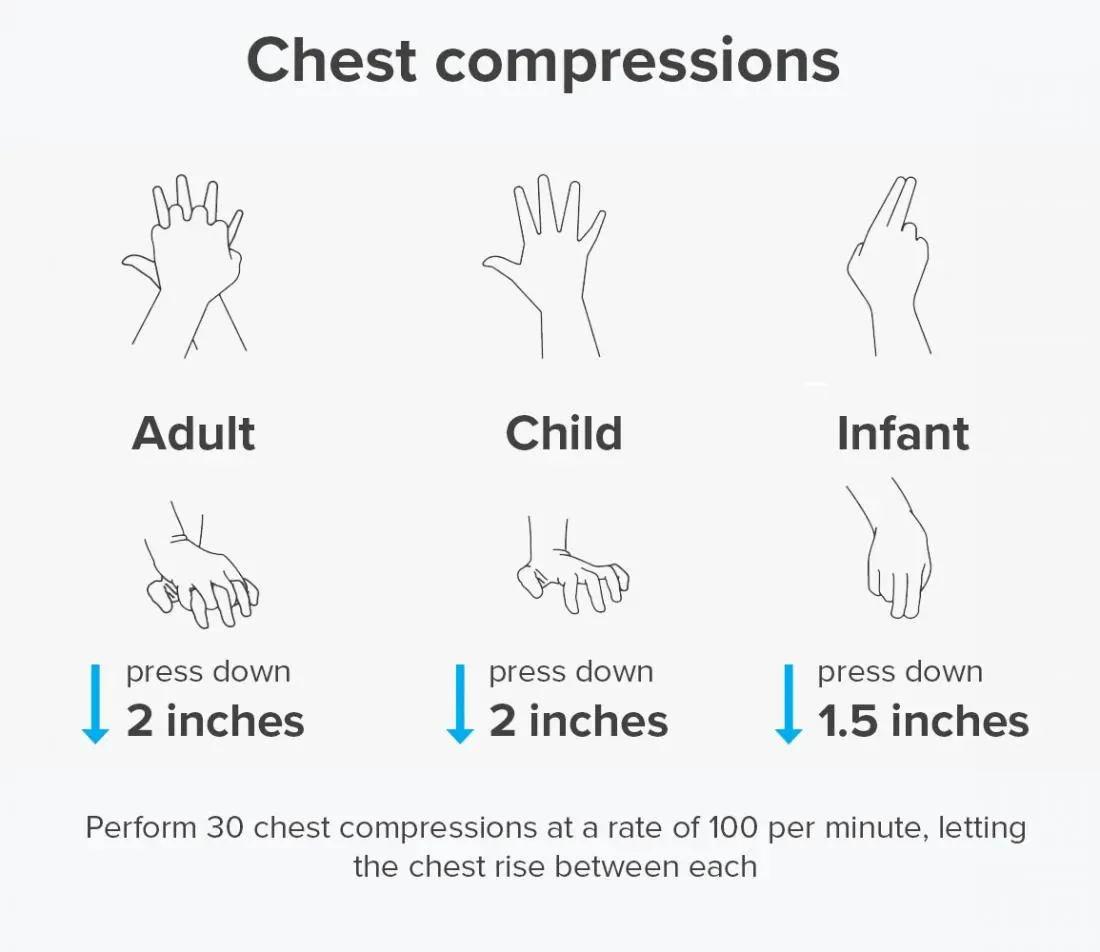
- Step 6: After each compression, let the chest come back to its normal position.
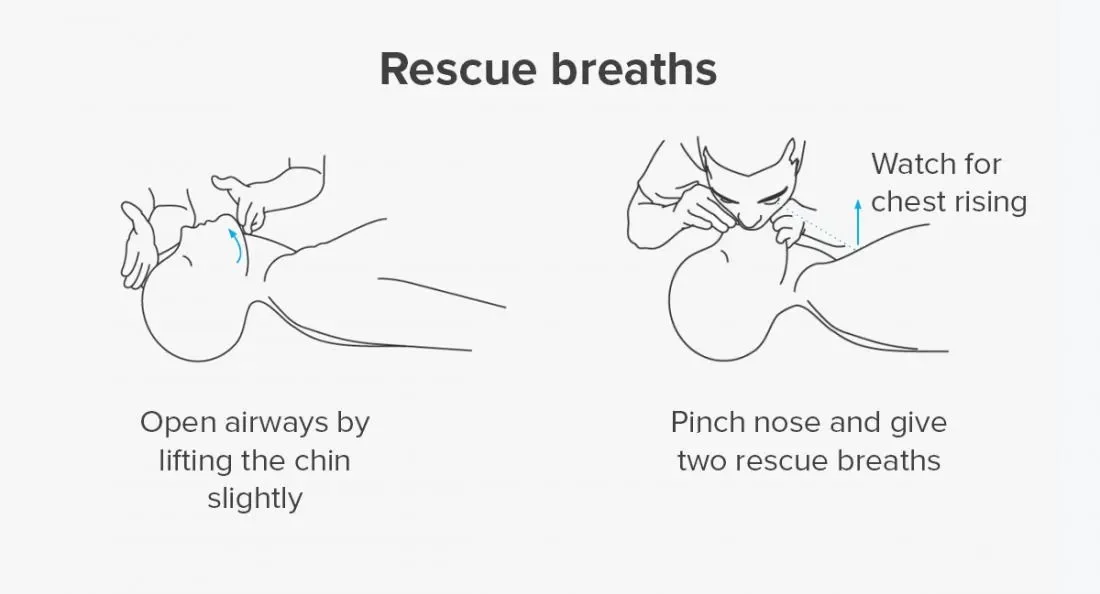
- Step 7: After every 30 compressions, give 2 slow rescue breaths. If more than one rescuer is present, after every 15 compressions, give 2 slow rescue breaths. Each given breath should be slightly over 1 second and give sufficient air to ensure visible chest rise.
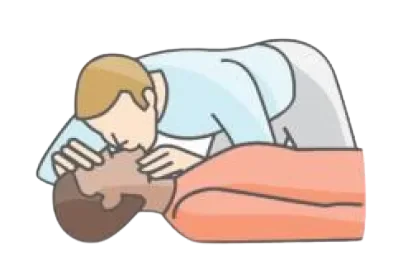
- Step 8: After five cycles of compressions, check for signs of circulation. If it is still absent, then continue another five cycles. Perform five cycles (approx. 2 minutes) of compression and ventilation (ratio 30:2). Switch the compressor at every 2 minute interval.
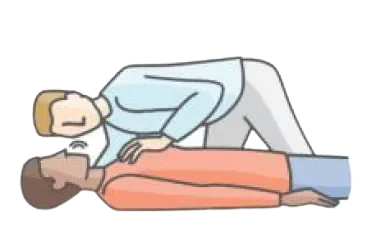
- Step 9: Before you start ventilation, open airway using a head tilt/chin lift manoeuvre (be careful in a patient with suspected neck injuries).
- Step 10: If the victim is breathing and circulation is present, keep the victim in recovery position and treat any life threatening injuries.
- Step 11: If the victim is still unconscious, not breathing and no pulse, continue the CPR till the victim is examined by a doctor or is taken to the hospital.
Flow Chart for Providing CPR